MOQ, or Minimum Order Quantity, refers to the smallest number of units a business is willing to sell to maintain profitability and operational efficiency. This article delves into the significance of MOQ, provides a guide on how to calculate the ideal MOQ for your products, and explains why it plays a crucial role in various business scenarios.
What is MOQ?
MOQ, or Minimum Order Quantity, is the lowest number of units a supplier is willing to sell for a given product. It can be defined by either a specific cost or quantity. For example, an MOQ might be set at $10,000 worth of milk or 1,000 liters of milk, depending on the supplier’s preferences.
A business typically determines its MOQ through careful analysis of profit margins, operational efficiency, and production requirements. Setting an MOQ helps ensure that every order is profitable and justifies the time and costs involved in fulfilling it.
High vs. Low Minimum Order Quantities: What It Means for Your Business
A high MOQ means the business requires customers to purchase larger quantities of a product. This typically indicates several factors:
- Low profit margins: When profit margins are slim, suppliers need to sell in large quantities to generate enough revenue.
- High shipping costs: Suppliers may face flat shipping rates for full truckloads or containers, so larger orders ensure profitability by filling available space.
- High customer acquisition costs: To offset the expense of gaining new customers, a higher MOQ ensures each transaction is profitable.
- High production costs: Expensive or time-consuming manufacturing processes increase costs, making a high MOQ necessary to maintain profitability.
- High administrative costs: Though not directly reflected in the cost of goods sold, higher administrative expenses can impact overall profitability, leading to a higher MOQ.
- High inventory costs: To reduce holding costs, companies may set a higher MOQ or offer bulk discounts to encourage faster inventory turnover.
A low MOQ, on the other hand, allows suppliers to sell smaller quantities while still maintaining profitability. This is often possible when:
- Make-to-order production: Businesses producing high-value, custom-built items may set a low MOQ.
- High profit margins: Sufficient margins enable businesses to operate with lower MOQs.
- Low supplier MOQ: A lower MOQ from their own suppliers enables flexibility.
- Low supply chain costs: When transportation fees are minimal, small orders can still be shipped profitably.
- Direct-to-consumer (D2C) model: E-commerce businesses often operate without an MOQ, as their sales are typically smaller, individual purchases.
- Low overall costs: Businesses with lower production or administrative costs can afford a lower MOQ. However, achieving economies of scale may tie up cash flow and increase holding costs, limiting the ability to sustain a low MOQ.
Steps to Calculate Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) for Your Business
There isn’t a universal formula for calculating MOQ, as it varies depending on several factors unique to each business. Variables like shipping costs, production capacity, and customer demand can significantly influence the ideal MOQ for a product. For instance, your shipping carrier’s pricing tiers may impact how profitable different order volumes are for your business.
While no single formula applies to every scenario, a commonly used method for calculating MOQ is:
Total Cost of Order / Unit Cost of Product = Minimum Order Quantity

However, this simplified formula may not account for important factors such as customer demand or supplier costs. For a more accurate calculation, many companies consider the Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) formula, which helps determine the optimal reorder levels based on various cost factors. This data can then be used to set appropriate MOQs.
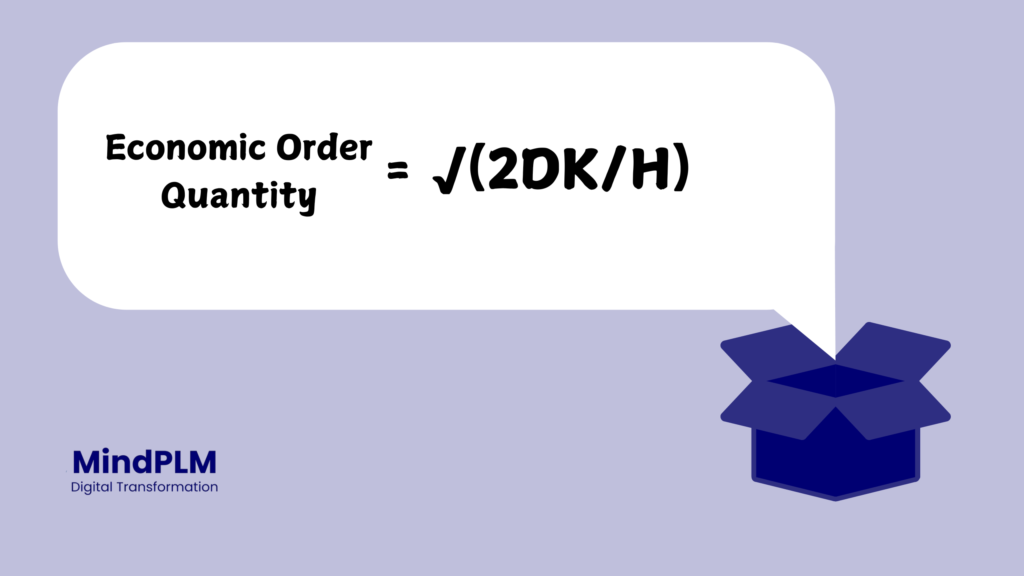
The EOQ formula is:
√(2DK/H) = Economic Order Quantity
Where:
- D = Annual demand (number of units purchased per year)
- K = Order cost per purchase order
- H = Annual holding cost per unit
By using EOQ, businesses can optimize reorder quantities and balance costs related to inventory management and customer demand, providing better insights into what the MOQ should be.
The Importance of MOQ for Manufacturers and Wholesalers
Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) is a crucial factor that directly influences a manufacturing or wholesaling business’s profitability, operational efficiency, and relationship with both suppliers and customers. Below are two key areas where MOQ plays a significant role:
Cost Efficiency
Maintaining cost efficiency is central to setting an effective MOQ. By understanding the minimum cost at which your business operates efficiently, you can make informed decisions about economies of scale in terms of order quantities, expenditures, and delivery schedules. This allows for better resource management and optimized production runs, ensuring that your business stays lean and cost-effective.
Profitability
A well-calculated MOQ is essential for safeguarding profitability. Without a proper MOQ, you risk over-ordering certain products and under-ordering others, leading to inventory imbalances and potential losses. An inaccurate MOQ can negatively impact profitability by increasing excess inventory costs or causing stockouts, which disrupt cash flow and sales. Setting the right MOQ ensures your operations remain profitable and efficient.
The Impact of Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) on Purchasers
It’s not only business owners who need to be concerned with Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ); purchasing officers should also pay close attention, as it directly impacts their procurement decisions, budget management, and overall strategy. Here are three key reasons why purchasers should care about MOQs:
Cost and Budget
Understanding the MOQ helps purchasers manage their budgets, cash flow, and forecasting more effectively. Knowing when to buy in larger quantities or when to minimize initial cash outlays is crucial in ensuring a balanced purchasing strategy that aligns with financial goals.
Planning
Purchasing in bulk, as determined by the MOQ, allows procurement managers to coordinate purchasing decisions with the company’s broader strategic objectives. Proper planning can improve inventory management and support the company’s long-term operational goals.
Availability of Items
Adhering to MOQ requirements ensures that sufficient inventory is available to meet customer demand. If the MOQ is miscalculated, it can lead to stockouts, causing customers to miss out on the products they need, which can result in lost sales for the business.
The Role of MOQ in Effective Inventory Management
Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) significantly impacts inventory management by influencing the cost-effective flow of goods, materials, and parts. The quantities at which products are ordered and sold affect storage costs, fulfillment times, and overall budget and forecasting. Here’s how MOQ interacts with various aspects of inventory management:
Supplier Negotiations
Maintaining strong relationships with suppliers is crucial for effective procurement. A good relationship allows for better negotiations and support during business fluctuations. By adhering to MOQs and communicating any changes promptly, you help keep these relationships positive and productive. Remember, suppliers also have MOQs, so ensuring your orders meet their requirements is essential for smooth operations.
Warehousing Management
MOQ plays a key role in determining how much inventory to hold. Accurate MOQ calculations help maintain the right stock levels—neither too much nor too little. This balance is crucial for meeting customer demand efficiently while avoiding excess storage costs. Proper inventory management based on MOQ contributes to cost savings and enhances profitability.
Customer Offerings
Adhering to optimal MOQs ensures you have enough product in stock to fulfill customer orders promptly. This results in efficient lead times and reliable deliveries, which boosts customer satisfaction. Consistently meeting customer needs helps build a positive reputation and strengthens brand awareness, leading to long-term business success.
Leveraging Inventory Management Software to Optimize MOQ
Automating the process of setting Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs) is made efficient with inventory management software. By integrating data from sales, inventory, and purchasing, this software helps determine the optimal stock levels for each product. Here’s how it works:
Data Collection and Analysis
Inventory management software automates the collection of crucial data, including sales trends, current inventory levels, and purchasing patterns. This automation reduces manual effort and increases accuracy in data analysis.
Dashboard Insights
The software presents data through intuitive dashboards, making it easy to interpret and act on. These visualizations help identify trends and patterns, enabling more informed decision-making regarding MOQs.
Determining Optimal MOQ Levels
With the insights gained from the software, you can set precise MOQ levels for each SKU. This optimization ensures that inventory levels are aligned with demand forecasts, reducing excess stock and minimizing stockouts. By leveraging automated tools, you achieve a more efficient and cost-effective inventory management process.
Key Factors Influencing MOQ and How to Find the Optimal Level
Determining the optimal Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) for each product involves navigating a range of fluctuating variables. Here are the key factors to consider:
1. Data Collection
Accurate historical data on inventory movement is crucial for setting effective MOQs. Begin tracking this data if you haven’t already, and review your MOQ levels after a few months to ensure they reflect current trends.
2. Supplier Costs
Understand all costs associated with your materials, parts, and products, including procurement, labor, and shipping. These costs impact your profitability and help determine your MOQ.
3. Warehousing Costs
The costs of storing inventory—such as warehousing, labor, and insurance—affect your profitability and fulfillment capabilities. These should be factored into your MOQ decisions to balance cost efficiency with inventory levels.
4. Customer Demand
Set MOQs that align with customer purchasing patterns. An MOQ too high above what customers typically buy can lead to unsold inventory and wasted resources.
5. Product Cost Fluctuations
Be aware that product costs can vary due to changes in supplier MOQs, internal cost structures, and other factors. Adjust your MOQ accordingly to accommodate these fluctuations.
6. External Factors
External events, such as extreme weather, natural disasters, or global pandemics, can impact supply and demand. These factors should be considered when setting MOQs to mitigate potential disruptions.
7. Technology
Utilize modern inventory management and forecasting tools to ensure your MOQs are based on the most accurate and up-to-date data available. Invest in contemporary systems within your budget to improve accuracy.
8. Regulatory Changes
Changes in regulations or legislation, such as minimum wage increases or inflation, can affect MOQs. Stay informed about regulatory developments to adjust your MOQs as needed.
Examples of Minimum Order Quantities in Various Industries
MOQ is utilized across various industries, but some sectors rely on it more heavily:
1. Clothing Industry
In the apparel sector, custom items like branded shirts or hats require significant design and production effort. MOQs help ensure that the cost of producing these items is justified by the order volume.
2. Food Sector
Food production businesses often set MOQs to optimize facility use. For instance, commercial ovens are not cost-effective for single-unit production, and growing a single vegetable for one customer is inefficient.
3. Cosmetics Industry
Cosmetics manufacturers invest time and resources in formulating specific products. Setting an MOQ helps protect against losses and ensures that production runs are economically viable.


